Most people think of toenails as purely cosmetic, but in reality, toenails serve an important protective function.
A good way to understand this is to think of a bicycle helmet or a hard hat. Just as a helmet protects your skull from impact, your toenail protects the small bone at the end of your toe, known as the distal phalanx.
This bone is surprisingly fragile and is located in a high-risk area of the body. The toes are frequently exposed to trauma, including objects falling, stubbing, sports injuries, or repeated pressure from footwear. The toenail acts as a rigid protective shield, absorbing and dispersing force away from the bone underneath.
The shape of the toenail is crucial. Rather than transmitting force directly downward, its curved structure helps spread impact sideways into the surrounding fibro fatty padding at the sides and underneath the toe. This load distribution significantly reduces the risk of fractures and crush injuries to the distal phalanx.
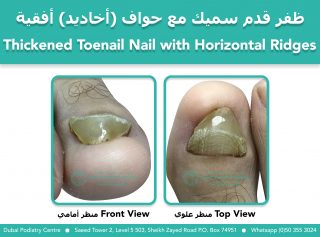
Why Do Toenails Become Thickened or Ridged?
Toenails are highly responsive to trauma. When the nail root, also known as the matrix, senses repeated stress or impact, it adapts by producing thicker nail material as a protective response.
Mild Repetitive Trauma
- Horizontal ridges or lines across the nail
- Gradual thickening over time
- Often caused by tight shoes, sports footwear, or work shoes
Single Significant Trauma
If you stub your toe hard or hit it against a wall, you may notice a horizontal ridge appearing several months later. This ridge represents a short period where the nail temporarily grew thicker to protect itself. Once the trauma stops, nail growth usually returns to normal.
When Thickened Toenails Signal a Footwear Problem
If one toenail, especially the big toenail or fifth toenail, becomes thick while the others remain normal, this often points to daily repetitive trauma rather than infection.
Common causes include:
- Shoes that are too tight or too narrow in the toe box
- Almond shaped or pointed shoes worn by people with square or broad forefeet
- Ill fitting work or safety shoes
With correct footwear, toenail thickness often begins to normalise. However, because toenails grow slowly, it can take around six months before you visibly see healthier nail growth from the root.
Sports, Slippage, and Toenail Damage
Even well fitting shoes can cause nail trauma if the foot slides forward inside the shoe.
This is common in:
- Tennis
- Padel
- Squash
- Badminton
- Downhill walking or hiking
Repeated forward movement increases pressure on the nail, sometimes leading to bruising beneath it. In more severe cases, blood may collect under the nail, known as a subungual haematoma.
If the trauma is strong enough, the nail may shed naturally after two to three months as a new nail grows underneath. Treatment is usually unnecessary unless the nail becomes painful, there are signs of infection, or the old nail fails to detach properly.
In these cases, a podiatrist can safely assist with nail removal and aftercare.
Tip. Cushioned sports or hiking socks with extra padding in the toe box can significantly reduce impact and prevent nail damage.
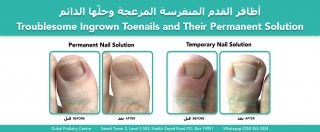
Curved and Involuted Toenails
Some toenails thicken not because of footwear, but because of their shape.
A healthy toenail resembles an upside down dinner plate.
Problem nails may resemble an upside down dinner bowl, curving excessively at the sides.
When a nail is too wide for the toe, it embeds into the surrounding skin, growth in length becomes restricted, and the nail thickens instead. Increased thickness causes more curvature, and more curvature causes more pressure. This vicious cycle often results in a very thick, involuted toenail.
In these cases, nail bracing alone is often ineffective unless the nail is aggressively thinned. The most reliable solution is a medial and lateral partial nail avulsion with phenolisation, often followed by a total nail avulsion. This allows a new, flatter nail of the correct width to grow back.
Toenail Trauma from Toe Hyperextension
Another overlooked cause of toenail thickening or separation is hyperextension of the toe.
When walking or running, the heel strikes the ground and the big toe lifts excessively upward. The nail repeatedly hits the roof of the shoe. This can happen even when shoe size is correct.
While taping or splinting may limit movement, it often leads to tendon strain or tendonitis because the muscle force remains strong.
In most cases, the safest approach is to allow natural toe movement and protect the nail with thick cushioned socks, particularly in the toe box.
Diabetic socks, hiking socks, and specialist padded sports socks are often very effective.
When to See a Podiatrist
You should seek professional assessment if a toenail continues to thicken despite correct footwear, one nail looks significantly different from the others, the nail is painful, curved, or repeatedly bruising, or a nail has detached or is not shedding normally.
Early assessment can prevent long term nail deformity and unnecessary procedures.
For more information or to book an appointment please call our clinic +971 4 3435390 or WhatsApp +971 50 3553024