 Your feet support the entire weight of your body and having healthy, pain free feet allows you to go anywhere and do anything without worrying about debilitating foot pain.
Your feet support the entire weight of your body and having healthy, pain free feet allows you to go anywhere and do anything without worrying about debilitating foot pain.
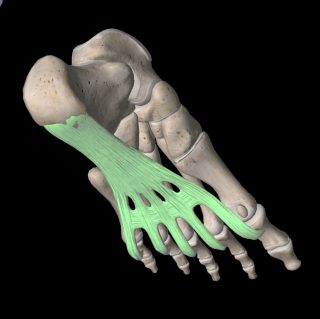
Your feet are made up of a complex network of bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, arteries and veins. To narrow down the cause of foot pain, let’s look at the areas of the foot you might experience pain. One of the most common foot areas for pain is the heel.
Plantar fasciitis
This is the most common cause of heel pain, reports Chief Podiatrist Michelle Champlin. The plantar fascia is an extremely tough band of fibrous tissue that connects your heel bone (calcaneum) to the front of your foot, just behind your toes.
Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain
The plantar fascia is similar to an emergency brake for your foot and can become irritated or inflamed when overused. This can happen when the muscles of your foot, particularly those forming the long arch of your foot, are untoned and not engaging properly when you run or walk. You may notice that your foot looks ‘flat’ due to the collapsed long arch.
Plantar fasciitis due to an underlying biomechanical cause can be assessed and diagnosed by your Podiatrist. Treatment may involve wearing custom corrective orthotics inside your work or leisure shoes, stretching and strengthening exercises and pain relieving NSAIDs. Dubai Podiatry Centre is the region’s only clinic which provides a one-stop service by qualified Podiatrists from assessing the patient, through to taking a mold of the patient’s feet, prescribing the correct orthotic, making them in-clinic in their own lab and then fitting them, as well as closely monitoring progress and making any ongoing adjustments required as your foot shape changes and foot pain reduces.
Repeated use of steroid injections should be avoided due to their reduction of the fatty padding in the heel, which will worsen the problem in the long run.
Fallen arches are not the only underlying cause of plantar fasciitis. Other common causes include very high arched foot types (pes cavus), sudden increase in exercise regime, wearing thin soled shoes such as ballet pumps or flip flops, a difference in leg lengths, short Achilles tendon, or an increase in bodyweight.
All of our bodies are unique, with different stresses and strains, so it’s important to see a qualified Podiatrist for heel pain to ensure treatment for the root cause and long-term resolution of the pain.
Other causes of heel pain can include heel spurs, stone bruises or Achilles tendonitis. Generalized foot pain, especially burning or tingling, should always be investigated thoroughly by your GP or Podiatrist, especially if your are diabetic. These can be signs of neuropathy, or nerve damage, and can signal that changes to your medication, diet or exercise routine are required.
For appointment, contact us:
Call: + 971 4 3435390
WhatsApp: + 971 50 355 3024
info@dubaipodiatry.com
To book online: Click here
ألم الكعب: هل هو التهاب اللفافة الأخمصية؟
تدعم قدميك وزن جسمك بالكامل، كما أن الحصول على أقدام صحية وخالية من الألم يسمح لك بالذهاب إلى أي مكان وفعل أي شيء دون القلق بشأن آلام القدم المنهكة.
تتكون قدميك من شبكة معقدة من العظام والعضلات والأوتار والأربطة والأعصاب والشرايين والأوردة. لتضييق نطاق سبب آلام القدم، دعونا نلقي نظرة على مناطق القدم التي قد تعاني من الألم. أحد أكثر مناطق القدم شيوعًا للألم هو الكعب
التهاب اللفافة الأخمصية
هذا هو السبب الأكثر شيوعًا لألم الكعب، وفقًا لتقارير رئيسة أطباء الأقدام ميشيل شامبلين. اللفافة الأخمصية عبارة عن شريط قوي للغاية من الأنسجة الليفية التي تربط عظم الكعب (العقبي) بمقدمة قدمك، خلف أصابع قدميك مباشرةً
التهاب اللفافة الأخمصية هو السبب الأكثر شيوعًا لألم الكعب
تشبه اللفافة الأخمصية فرامل الطوارئ لقدمك ويمكن أن تصبح متهيجة أو ملتهبة عند الإفراط في استخدامها. يمكن أن يحدث هذا عندما تكون عضلات قدمك، خاصة تلك التي تشكل القوس الطويل لقدمك، غير متماسكة ولا تعمل بشكل صحيح عند الجري أو المشي. قد تلاحظ أن قدمك تبدو “مسطحة” بسبب القوس الطويل المنهار
يمكن تقييم وتشخيص التهاب اللفافة الأخمصية الناتج عن سبب ميكانيكي حيوي أساسي من قبل طبيب الأقدام الخاص بك. قد يشمل العلاج ارتداء أجهزة تقويم العظام التصحيحية المخصصة داخل أحذية العمل أو الترفيه، وتمارين التمدد والتقوية ومضادات الالتهاب غير الستيروئيدية المخففة للألم. مركز دبي لعلاج الأرجل هو العيادة الوحيدة في المنطقة التي تقدم خدمة شاملة من قبل أطباء الأقدام المؤهلين بدءًا من تقييم المريض وحتى أخذ قالب لقدم المريض ووصف جهاز تقويم العظام الصحيح وجعله داخل العيادة في مختبره الخاص ومن ثم تركيبه. لهم، بالإضافة إلى مراقبة التقدم عن كثب وإجراء أي تعديلات مستمرة مطلوبة مع تغير شكل قدمك وتقليل آلام القدم
يجب تجنب الاستخدام المتكرر لحقن الستيرويد لأنها تقلل من الحشوة الدهنية في الكعب، مما يؤدي إلى تفاقم المشكلة على المدى الطويل
الأقواس المتساقطة ليست السبب الوحيد الكامن وراء التهاب اللفافة الأخمصية. تشمل الأسباب الشائعة الأخرى أنواع القدم المقوسة جدًا (pes cavus)، أو الزيادة المفاجئة في نظام التمارين الرياضية، أو ارتداء أحذية ذات نعل رفيع مثل أحذية الباليه أو النعال، أو الاختلاف في أطوال الساق، أو قصر وتر العرقوب، أو زيادة في وزن الجسم
جميع أجسامنا فريدة من نوعها، مع ضغوطات وتوترات مختلفة، لذلك من المهم رؤية طبيب أقدام مؤهل لعلاج آلام الكعب لضمان علاج السبب الجذري للألم وحله على المدى الطويل
يمكن أن تشمل الأسباب الأخرى لألم الكعب نتوءات الكعب أو الكدمات الحجرية أو التهاب وتر العرقوب. يجب دائمًا فحص آلام القدم العامة، وخاصة الحرق أو الوخز، بدقة من قبل طبيبك أو طبيب الأقدام، خاصة إذا كنت مصابًا بالسكري. يمكن أن تكون هذه علامات على الاعتلال العصبي أو تلف الأعصاب، ويمكن أن تشير إلى ضرورة إجراء تغييرات على الدواء أو النظام الغذائي أو روتين التمارين الرياضية
لحجز موعد، تواصل معنا: الهاتف: ٠٤٣٤٣٥٣٩٠
واتساب: ٠٥٠٣٥٥٣٠٢٤
البريد الإلكتروني: info@dubaipodiatry.com
لحجز موعد عبر الإنترنت: اضغط هنا







 Your feet support the entire weight of your body and having healthy, pain free feet allows you to go anywhere and do anything without worrying about debilitating foot pain.
Your feet support the entire weight of your body and having healthy, pain free feet allows you to go anywhere and do anything without worrying about debilitating foot pain.