
Written by Michelle Champlin BSc Pod., M.Ch.S., S.R., Ch., (UK)
Your calcaneum, or heel bone is the first part of your body to hit the ground while walking – the ‘heel strike’. Fractures, or breaks to the bone itself are a more unusual cause of heel pain. Other more common causes are plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis and heel spurs, or Sever’s Disease in children.
The heel bone is like a hard boiled egg – it has a thin but hard outer ‘shell’ and a more spongy, softer bone within. The main cause of heel fractures are accidents such as falling onto your heels from a height such as a ladder, or impact during a car crash. Sometimes the heel bone can suffer from stress fractures due to repeated impact over time.
The calcaneum forms the ‘sub-talar’ joint with the talus and cuboid bones
The heel bone connects to two other bones – the talus and the cuboid, as you can see in the picture. These three bones form the sub-talar joint, which controls much of your foot during motion from walking to running and can be a main cause of ‘flat feet’ when the joint allows the foot to ‘over-pronate.’
When serious injuries break not just the heel bone, but also involve this sub-talar joint and it’s ligaments, muscles or tendons, this can be a more complex and difficult injury to mend.
The signs and symptoms of a heel bone fracture depend on where the bone is fractured, how it happened and how severe it is. As with most bone fractures, you will notice pain and swelling to the heel area, with immediate pain if it was a traumatic injury.
To diagnose the injury, the Podiatrist, GP or orthopaedic foot surgeon will take a full history, including events that led up to the pain to understand the mechanism of the injury, physically examine your foot and ankle and order x-rays.
X-ray image of a fractured calcaneum
Treatment for fractured heel bones will depend on the type of fracture and severity. This will indicate whether or not surgery is required.
Non-surgical treatments can include:
• Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation
• Immobilization and weight being taken off the heel, using a device such as an Aircast
Following healing of the fracture, you may be advised custom orthotic shoe inserts that may be required to correct foot posture and alignment and to tone up underused ligaments and muscles following immobilization. This type of rehabilitation will also likely be advised after surgery too for more serious fractures. Any foot or ankle injury, even ankle sprains from years ago, can have long lasting detrimental effect on your foot and ankle posture (including stiffness, arthritis and pain), so it is important to have any form of heel, foot or ankle pain thoroughly investigated by your Podiatrist.
If you suspect a fractured heel bone, or if you have recovered from a foot or ankle sprain or fracture it is advisable to have your alignment reviewed by a Podiatrist in order to avoid longer-term complications.
Appointments with the leading UK qualified Podiatrists at Dubai Podiatry Centre, led by Chief Podiatrist Michelle Champlin and based on Sheikh Zayed Road, can be made by contacting +971 4 3435390. The Clinic is conveniently located near DIFC Metro station and is open every day except Fridays. If driving, Dubai Podiatry Centre is also listed on the Dubai map app for android and iPhones, Makani.
بقلم ميشيل شامبلين
عظم الكعب أو عظم الكعب هو الجزء الأول من جسمك الذي يضرب الأرض أثناء المشي – “ضربة الكعب”. تعتبر الكسور أو الكسر في العظم نفسه سببًا غير عادي لألم الكعب. الأسباب الأخرى الأكثر شيوعًا هي التهاب اللفافة الأخمصية، أو التهاب وتر العرقوب، أو مرض سيفر عند الأطفال.
يشبه عظم الكعب البيضة المسلوقة – فهو يحتوي على “قشرة” خارجية رقيقة ولكنها صلبة وعظم أكثر إسفنجية ونعومة في الداخل. السبب الرئيسي لكسور الكعب هو الحوادث مثل السقوط على كعبك من ارتفاع مثل السلم، أو الاصطدام أثناء حادث سيارة. في بعض الأحيان يمكن أن يعاني عظم الكعب من كسور الإجهاد بسبب التأثير المتكرر مع مرور الوقت.
يشكل العقبي المفصل “تحت الكاحل” مع عظام الكاحل والعظام المكعبة
ويتصل عظم الكعب بعظمتين أخريين – الكاحل والمكعب، كما ترون في الصورة. تشكل هذه العظام الثلاثة المفصل تحت الكاحل، الذي يتحكم في جزء كبير من قدمك أثناء الحركة من المشي إلى الجري ويمكن أن يكون السبب الرئيسي لـ “القدم المسطحة” عندما يسمح المفصل للقدم “بالكب الزائد“.
عندما لا تقتصر الإصابات الخطيرة على كسر عظم الكعب فحسب، بل تشمل أيضًا هذا المفصل تحت الكاحل والأربطة أو العضلات أو الأوتار، فقد تكون هذه إصابة أكثر تعقيدًا وصعوبة في الإصلاح.
تعتمد علامات وأعراض كسر عظم الكعب على مكان كسر العظم وكيفية حدوثه ومدى خطورته. كما هو الحال مع معظم كسور العظام، ستلاحظ ألمًا وتورمًا في منطقة الكعب، مع ألم فوري إذا كانت إصابة مؤلمة.
لتشخيص الإصابة، سيأخذ طبيب الأقدام أو الطبيب العام أو جراح عظام القدم تاريخًا كاملاً، بما في ذلك الأحداث التي أدت إلى الألم لفهم آلية الإصابة، وفحص قدمك وكاحلك جسديًا وطلب الأشعة السينية
صورة بالأشعة السينية للعظم المكسور
يعتمد علاج عظام الكعب المكسورة على نوع الكسر وشدته. سيشير هذا إلى ما إذا كانت الجراحة مطلوبة أم لا.
يمكن أن تشمل العلاجات غير الجراحية ما يلي:
• الراحة والثلج والضغط والرفع
• تثبيت ورفع الوزن عن الكعب باستخدام جهاز مثل جهاز Aircast
بعد شفاء الكسر، قد يُنصح باستخدام أحذية تقويمية مخصصة قد تكون مطلوبة لتصحيح وضعية القدم واستقامتها ولشد الأربطة والعضلات غير المستخدمة بعد تثبيت الحركة. من المحتمل أيضًا أن يُنصح بهذا النوع من إعادة التأهيل بعد الجراحة أيضًا للكسور الأكثر خطورة. أي إصابة في القدم أو الكاحل، حتى الالتواء في الكاحل منذ سنوات، يمكن أن يكون لها تأثير ضار طويل الأمد على وضعية قدمك وكاحلك (بما في ذلك التيبس والتهاب المفاصل والألم)، لذلك من المهم علاج أي شكل من أشكال آلام الكعب أو القدم أو الكاحل بشكل كامل. التحقيق من قبل طبيب الأقدام الخاص بك.
إذا كنت تشك في وجود كسر في عظم الكعب، أو إذا كنت قد تعافيت من التواء أو كسر في القدم أو الكاحل، فمن المستحسن أن تقوم بمراجعة استقامتك من قبل طبيب الأقدام لتجنب المضاعفات على المدى الطويل.
يمكن حجز المواعيد مع أبرز أطباء الأقدام المؤهلين في المملكة المتحدة في مركز دبي لعلاج الأقدام، بقيادة رئيس أطباء الأقدام ميشيل شامبلين ومقره في شارع الشيخ زايد، عن طريق الاتصال بالرقم ٠٤٣٤٣٥٣٩٠. تقع العيادة بالقرب من محطة مترو مركز دبي المالي العالمي وهي مفتوحة كل يوم باستثناء أيام الجمعة. إذا كنت تقود السيارة، فإن مركز دبي لعلاج الأرجل مدرج أيضًا على تطبيق خرائط دبي لأجهزة أندرويد وآيفون، مكاني.


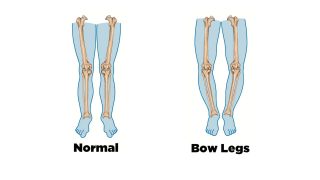
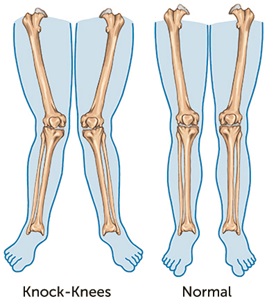 Genu Valgum is the medical term for when legs appear ‘knock knee’ and the knees angle inwards and the lower leg angles outwards. (This is the opposite condition to Genu Varus, or bowlegs – you can find out more about this here). ‘Genu’ means ‘knee’ in Latin and ‘Valgum’ means outwards. Hence, there are a number of ‘valgus’ conditions, including Hallux Valgus (bunions) – toe outwards.
Genu Valgum is the medical term for when legs appear ‘knock knee’ and the knees angle inwards and the lower leg angles outwards. (This is the opposite condition to Genu Varus, or bowlegs – you can find out more about this here). ‘Genu’ means ‘knee’ in Latin and ‘Valgum’ means outwards. Hence, there are a number of ‘valgus’ conditions, including Hallux Valgus (bunions) – toe outwards.


