Gout
Written by Michelle Champlin BSc Pod., M.Ch.S., S.R., Ch., (UK)
What is gout?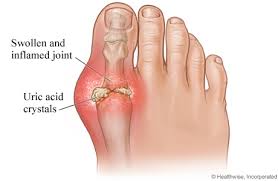
Gout is a medical condition caused by increased levels of uric acid in the bloodstream. The uric acid crystallizes, and these crystals then collect in joints, tendons and surrounding soft tissue. Gout has been called the ‘disease of kings’ due to its association with a rich diet. King Henry VIII of England was a well-known sufferer.
The joint at the ball of the big toe – the metatarso-phalangeal joint (MTP joint) – is most commonly affected. Gout results in recurrent painful ‘flare-ups’ of inflammatory arthritis. The affected joint, in over 50% of cases at your big toe, becomes hot, swollen and tender. However, other joints such as the heels, knees, wrists and fingers can be affected.
Gout is unfortunately becoming more common, with 1-2% of the population being affected. This increase may be due to:
• Longer life expectancy
• Dietary changes
• Increase in metabolic syndromes (such as hypertension, diabetes)
People with gout frequently have other conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes and heart disease. It’s therefore important to see your GP as soon as you suspect you may have gout. They will carry out necessary diagnostic tests, recommend a course of short-term medication to alleviate and advise on longer term dietary and lifestyle changes to control the gout as well as any other co-existing conditions such as diabetes.
Symptoms
• Pain usually worse at night (due to the body’s lower temperature)
• Long-term gout can cause permanent hard, painless deposits of crystals at the joints, called tophi
• Tophi can result in damage to the bones – arthritis
• Crystals collecting in the kidneys can cause kidney problems, including kidney stones
Causes of Gout
• Lifestyle (including diet rich in seafood, alcohol, fructose-sweetened drinks, meat)
• Physical trauma / surgery
• Genetics
• Under-excretion of urea by the kidneys
Gout is confirmed by a test at your GP – the characteristic uric acid crystals will be visible in your joint fluid. X-rays can be helpful in someone with chronic gout.
Gout Treatment
During an acute attack, treatment tends to consist of:
• Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
• Steroids
• Colchicine
Long term, gout is controlled by diet and lifestyle changes. Consuming coffee, Vitamin C and dairy products are understood to lower the risk. Being more active and increasing your fitness also helps. Aim to lose weight if you’re overweight. Avoid fructose based drinks and other food triggers such as alcohol (especially beer and spirits), meat and seafood.
If you do experience pain to your big toe joint, or any area of your foot or leg, you can also make an appointment with the expert Podiatrists at Dubai Podiatry Centre on +971 4 3435390. Your Podiatrist can also rule out any other issues that can appear similar to gout, even biomechanics issues causing big toe pain such as hallux rigidus or bunions. If necessary, they can also refer you to an appropriate specialist, such as a rheumatologist, your GP or an orthopaedic surgeon, depending on diagnosis, investigation and treatment required.

